For savvy cryptographic currency investors, there is nothing more satisfying than staking your tokens and earning that juicy, juicy yield. With Ethereum’s transition to a full Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus model, $ETH itself has become one of these aforementioned yield-bearing assets.
"Ultra-sound money."
Unfortunately, native $ETH staking does have certain limitations which has paved the way for Liquid Staking Derivatives. This little article will briefly cover the LSD concept and go over some of the protocols on the market.
I. What are Liquid Staking Derivatives (LSDs)?
Let’s start with a quick overview of derivatives in traditional finance.
A derivative is a contract between two parties and its price is determined by fluctuations in the underlying asset. There are derivatives on almost anything tradable that you can think of. The most common types of derivatives are futures, options, forwards and swaps.
Derivatives in Crypto
At the beginning, derivatives were primarily strived to hedge one specific position over an underlying asset. It basically can be seen as a form of insurance. In the crypto market, the underlying asset in derivatives trading can be any token. Two parties that enter into a financial contract speculate on the cryptocurrency’s price on a future date. During the very first phase of the contract, the sides agree on a buying/selling price for the tokens on a specific day, regardless of the market price. As a result, investors can profit from changes in the underlying asset’s price by purchasing the currency at a cheaper price and selling it at a higher price.
Derivative staked tokens represent a claim on the underlying, illiquid staking positions, which are nevertheless subject to the protocol limits. These tokenized and thus liquid claims can be employed in a variety of financial products. As a result, stakers may be able to earn higher returns or more easily manage their risk exposure in a variety of ways, such as by reducing the risks associated with validators.
Liquid Staking Derivatives
Liquid Staking Derivatives are a type of derivative contract that allows users to stake their assets in order to receive a return on their investment. These derivatives are designed to be liquid, meaning that users can retain liquidity of their tokens even though they are locked in the blockchain. As such, users can easily enter and exit the contracts without having to wait for a long period of time.
This makes them attractive to investors who are looking for a way to earn a return on their assets without having to lock it up for a long period of time. It is popular in decentralized finance (DeFi) because these derivative tokens can be used elsewhere to generate extra yield: investors can use staked assets in the ecosystem for lending, trading, and as collateral, hence lowering the opportunity cost of locking assets up for staking.
II. Ethereum: Shanghai Upgrade
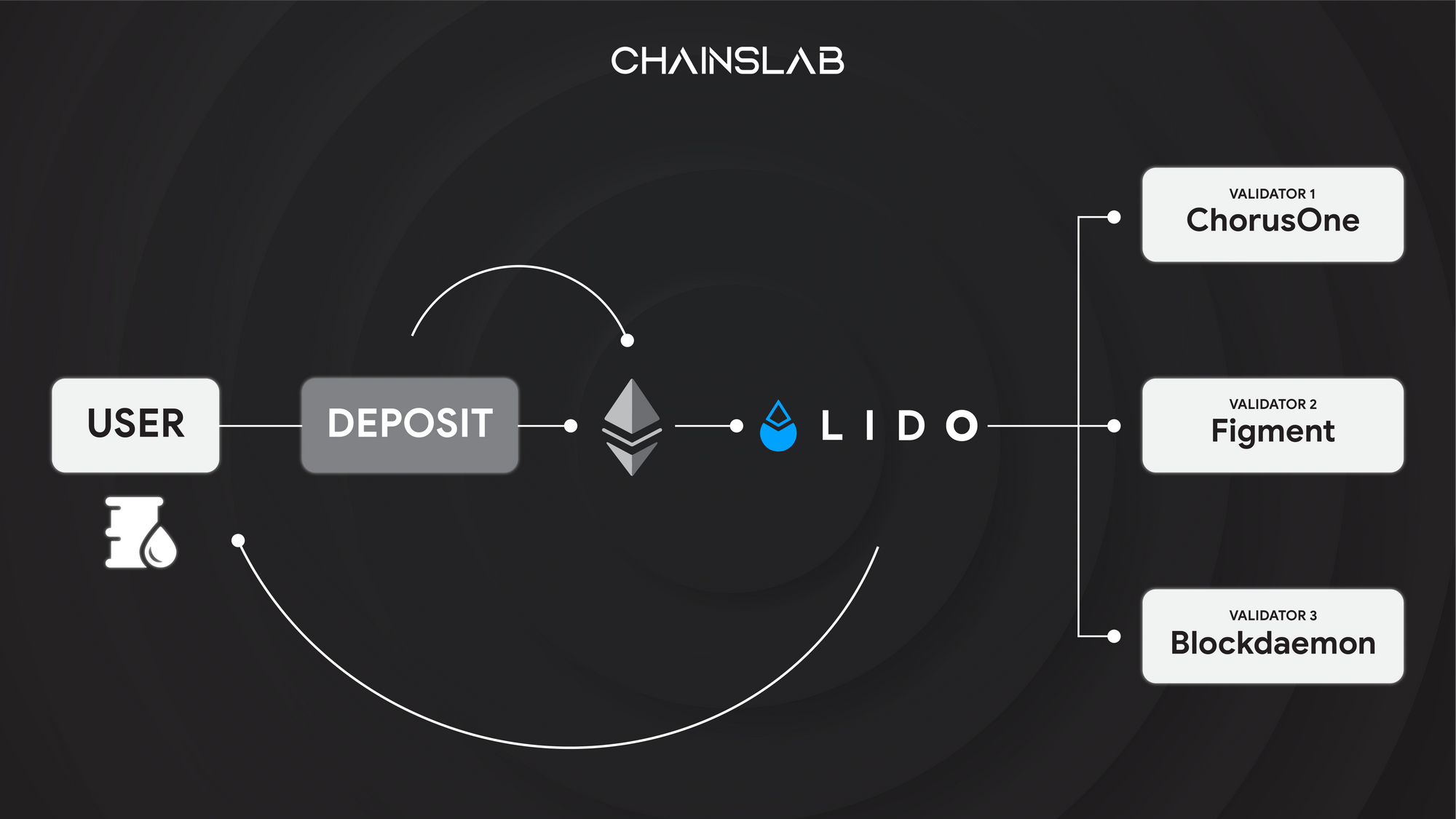
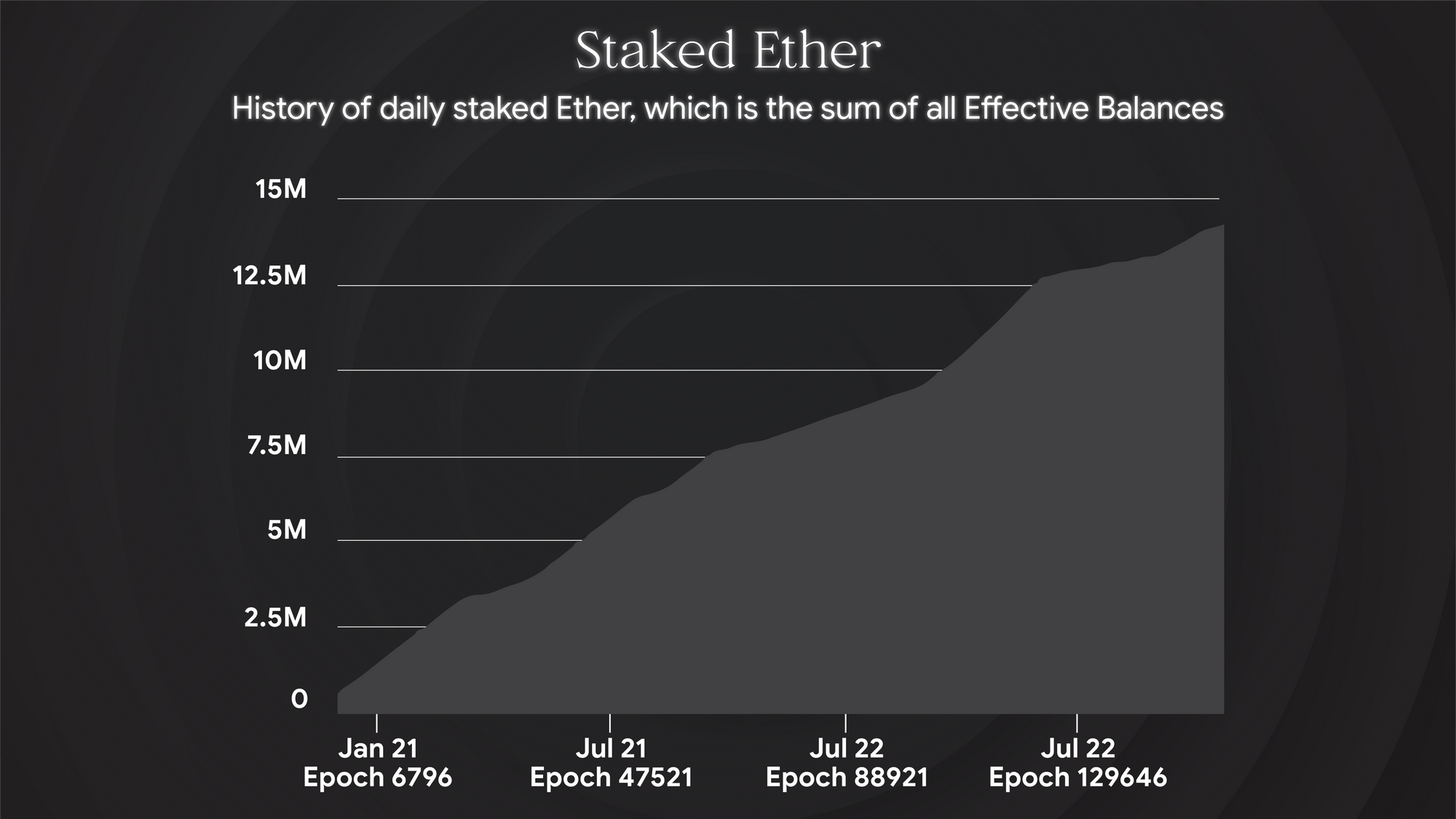
Despite Ethereum being the leading proof-of-stake blockchain, it only has a staking ratio of 14% according to Ethscan, which is a lot lower compared to otherLayer-1 blockchains including Cardano, BNB Chain, and Solana. This is mainly because of its entry barrier for staking. Since ETH is pooled, not everyone has 32 ETH to become a validator. Therefore, liquid staking protocols such as Lido, Rocket Pool, and Ankr Protocol allow ETH holders to stake without running a validator node.
The Shanghai Upgrade is designed to significantly reduce the risk and opportunity cost for validators to stake their ETH, as the minimum duration for staking will fall to just 27 hours. As a result, Ethereum’s staking ratio should reach parity with other leading blockchains after the update. This will also provide market opportunity for growth of liquidity staking protocols.
The update brings a lot of flexibility to investors, allowing them to stake their ETH and earn rewards elsewhere as well. Therefore, liquidity hunting will be a popular option to earn more yields, as investors look to use their newly unstaked ETH in other DeFi protocols, especially Liquidity Staking Derivatives.
III. Benefits of LSD
- No Risk of Impermanent Loss: When lending assets to liquidity pools you run the risk of impermanent loss. This is a common risk of various yield earning strategies involving liquidity pools, but with liquid staking this isn’t something you have to worry about.
- Enhanced Decentralization: Most protocols will not only run the validator nodes for you, but also choose reliable validator nodes they trust. This decentralizes the network for everyone, by spreading the influence of the network to a large number of nodes. Which further decreases the potential for a single centralized party to influence transactions or build up to the infamous 51% attack.
- Transfer of Risks to the Protocol You are Using: With delegated proof of stake you have the option to choose a validator node that you deem trustworthy to not get slashed. It can be difficult to do your own research with delegated nodes. Fortunately, liquid staking takes this off your plate, because you hand all node slashing risk over to your protocol of choice (As can be seen at ANKR). Basically, this means that if a node that the protocol chose gets slashed, they’re the ones that have to cover the loss, not you!
- Immediate Access to Liquidity / Yield-Earning Opportunities: The ability to use your ETH while it’s staked is perhaps the most significant benefit of liquid staking. Because your ETH remains liquid, you unlock the opportunity to earn yield through other DeFi lending strategies on top of that. These strategies range everywhere from liquidity mining & yield farming to lending your assets to protocols and vaults.
All things considered, liquid staking is a low risk, medium reward DeFi investing strategy. Unlike complex yield-earning strategies, liquid staking is simple and doesn’t require any technical knowledge or entail risk of impermanent loss. You can start with however much you’re willing to invest and start receiving rewards immediately. The rewards are nothing huge, but again the higher the reward the higher the risk.
IV. Risks of LSD
Whilst LSDs eliminate the need for large sums of capital and loss of tradability for principal and rewards, there are risks associated with non-native staking.
- Smart contract hacks and exploits: Reliance on third party protocols may confer additional smart contract risk on your funds. Coding errors and exploits are definitely things to be considered if you want to use one of these services. In addition, since rewards and principal of the backing ETH are locked until Etheruem’s Shanghai update, there is a level of uncertainty regarding the timeline for withdrawal.
- Risk of depeg: Since LSDs are represented by ERC-20 tokens, depeg risk is another thing to give some thought to. Whilst LSDs are conceptually backed 1:1 by ETH (either represented 1:1 or via an index), they are priced by standard AMM logic. In the event of an unbalanced liquidity pool, LSDs may be traded for less than their backing value.
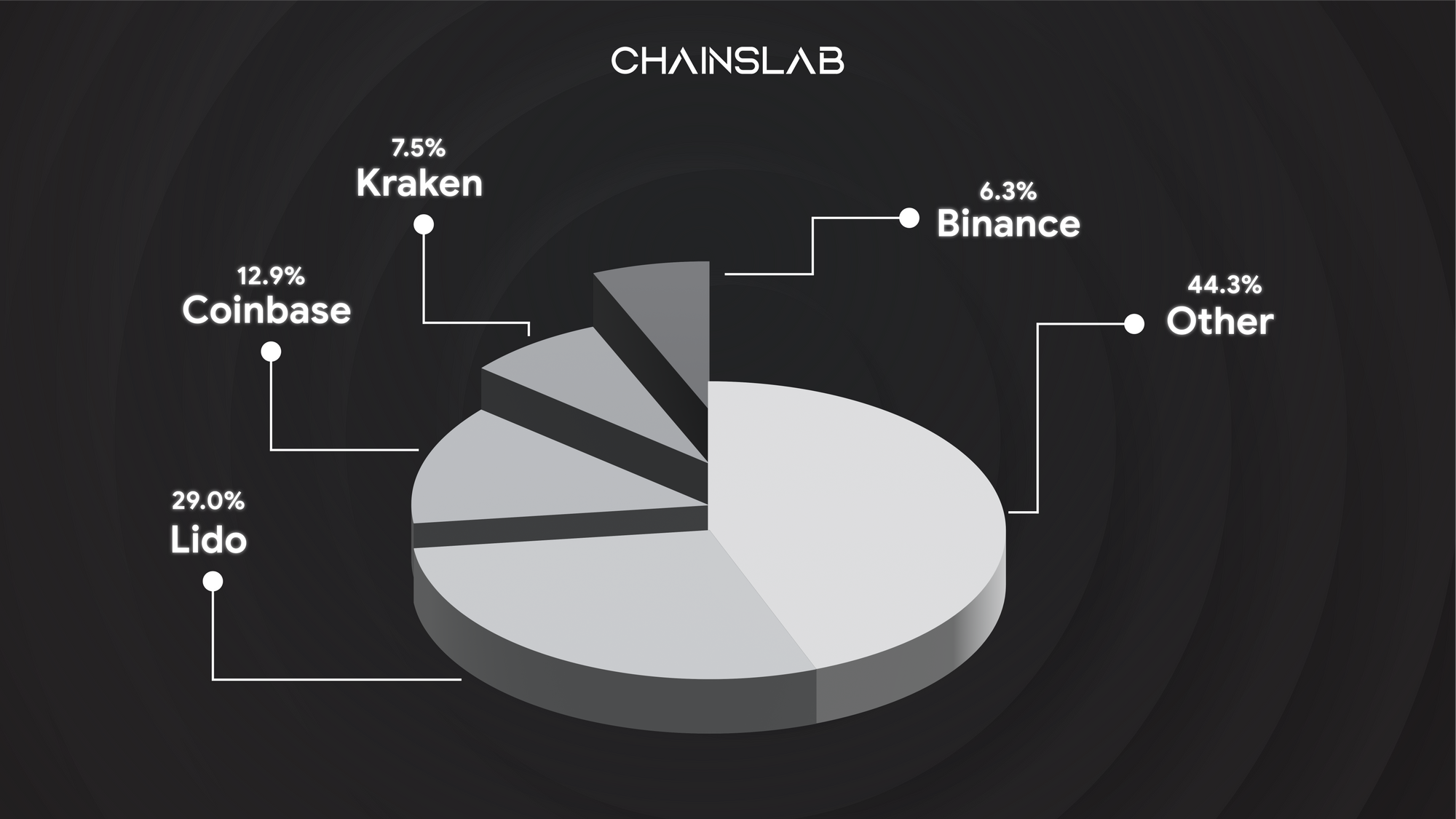
- Centralized vs. decentralized liquid staking: users of liquid staking protocols should consider whether their choice to stake with a dominant protocol like Lido or a large centralized exchange contributes to the centralization of the blockchain, making it less valuable overall.
V. Conclusion
Liquid staking brings stakers the benefits of immediate liquidity, composability of staked assets, and distribution of stake across multiple validators. However, the market’s liquidity for liquid staking tokens is limited, and stakers take on custody risk or smart contract risk, depending on their choice between a centralized or decentralized provider.
For Ethereum, the benefits of liquid staking have encouraged more of the supply to become staked, at the possible expense of decentralization. The benefits of liquid staking extend to many blockchains, however, and the growth of liquid staking pools is an ongoing trend.
It is also important to pay attention to the narrative surrounding Liquid Staking Derivatives, as it could potentially have significant impacts on the market. It is advisable to carefully consider your options and approach, as well as to be aware of the potential for fluctuation in the coming year. When it comes to Ethereum, it may be wise to consider buying upon hearing rumors and selling before any major announcements.